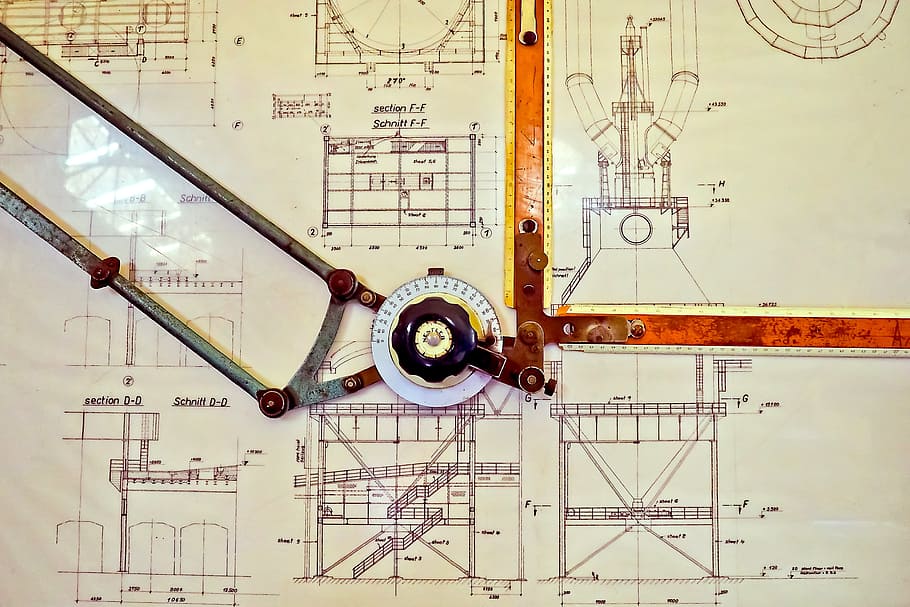
SolidWorks/FreeCAD Practice: Complete 3D Modeling from Workshop Drawings
📅 Estimated Time: 45-60 minutes per drawing
📐 Skill Level: Beginner to Intermediate
🎯 Goal: Develop technical drawing reading skills and 3D modeling proficiency
🎯 Introduction to the Exercise Series
In this comprehensive practice series, we'll use 10 workshop technical drawings with complete dimensions for 3D modeling practice in SolidWorks or FreeCAD. This exercise is perfect for:
- 💡 Beginners wanting to practice technical drawing interpretation
- 🔄 Experienced users looking to sharpen rapid modeling skills
- 🎓 Students preparing for CAD examinations
- 🏭 Engineers maintaining and developing design skills
📐 Workshop Drawings for Practice
Here are 10 technical drawings we'll use in this exercise series. Click on each image for larger view:
Drawing 0011: Bracket with Multiple Holes

Features: Linear patterns, hole features, fillets
Difficulty: Easy
Drawing 0012: Complex Section View Part

Features: Section views, advanced dimensions
Difficulty: Medium
Drawing 0013: Bent Tube Profile

Features: Sweep features, bend radii
Difficulty: Easy
Drawing 0015: Angular Bracket

Features: Angular dimensions, R40 radius
Difficulty: Medium
Drawing 0016: Complex Assembly Part

Features: Multiple features, R8 fillets, complex geometry
Difficulty: Hard
Drawing 0017: Symmetrical Housing

Features: Symmetry, linear patterns, A20 annotation
Difficulty: Medium
Drawing 0018: Sectional Bearing Block

Features: Section views, R1 fillets, complex cuts
Difficulty: Hard
Drawing 0019: Simple Mounting Plate

Features: Basic extrusion, hole patterns
Difficulty: Easy
🔧 Step-by-Step Modeling Approach
1 Analyze the Technical Drawing
Before starting modeling, carefully analyze the drawing:
- Identify main dimensions and tolerances
- Study all views (front, top, side, isometric)
- Note all holes, cuts, fillets, and chamfers
- Understand material specifications
- Identify datum references and critical features
💡 Pro Tip: Use different colors to highlight various features on the drawing before starting modeling. This helps in planning your feature tree.
2 Create Base Sketch in SolidWorks/FreeCAD
For SolidWorks Users:
1. File → New → Part
2. Select appropriate plane (Front, Top, Right)
3. Start 2D Sketch
4. Use Line, Circle, Rectangle tools
5. Add Smart Dimensions from drawing
6. Apply geometric relations (Horizontal, Vertical, Equal)
7. Exit Sketch → Extruded Boss/Base
For FreeCAD Users:
1. Create New → Part Design
2. Create Body → Create Sketch
3. Select appropriate plane (XY, XZ, YZ)
4. Use geometry creation tools
5. Add Constraints (dimensions)
6. Apply geometric constraints
7. Pad (extrude) the sketch
3 Add Secondary Features and Details
After base extrusion, add all secondary features:

Hole Features: Use Extruded Cut or Hole Wizard

Fillets & Chamfers: Add edge treatments
4 Advanced Features and Final Touches
Add advanced features according to drawing specifications:
SolidWorks Advanced Features:
- Revolved Boss/Base for rotational parts
- Swept Boss/Base for complex paths
- Lofted Boss/Base for transitional shapes
- Mirror and Pattern features for symmetry
- Reference Geometry for complex alignments
🎯 Modeling Strategies by Difficulty
| Difficulty |
Recommended Approach |
Time Estimate |
Key Challenges |
| Easy |
Single sketch + extrude + basic features |
15-25 minutes |
Basic dimension interpretation |
| Medium |
Multiple sketches + features + patterns |
30-45 minutes |
Feature order, relations management |
| Hard |
Complex sketches + advanced features + sections |
45-60+ minutes |
Section views, complex geometry |
⚡ Advanced Modeling Techniques
Parametric Modeling
Use parameters for easier modifications:
// SolidWorks Equations Example
"D1@Sketch1" = 100mm
"D2@Sketch1" = 50mm
"fillet_radius" = 5mm
"hole_pattern_count" = 4
Design Tables & Configurations (SolidWorks)
Create different variations of the part:
- Configuration Manager → Add Configuration
- Different dimensions for each configuration
- Different materials and appearances
- Suppress/unsuppress features
Assembly Techniques
For multi-part drawings:
1. Create individual parts
2. New Assembly → Insert Components
3. Apply Mates (Coincident, Concentric, Distance)
4. Check for interference
5. Create exploded views if needed
📊 Accuracy Verification Checklist
After completing each model, verify accuracy:
| Parameter |
On Drawing |
In Model |
Verification Method |
| Overall Length |
As specified |
Measure Tool |
✅ Correct / ❌ Incorrect |
| Hole Diameters |
As specified |
Measure Tool |
✅ Correct / ❌ Incorrect |
| Fillet Radii |
R values |
Fillet Feature |
✅ Correct / ❌ Incorrect |
| Material Volume |
Calculate |
Mass Properties |
✅ Within Tolerance |
| Center of Mass |
N/A |
Mass Properties |
✅ Logical Position |
💡 Efficiency Tips for Professional Modeling
🔥 Pro Tip 1: Always use "Fully Defined" sketches in SolidWorks (sketch should be black, not blue) to avoid unexpected changes.
🔥 Pro Tip 2: Use geometric relations (Horizontal, Vertical, Equal, Parallel) before adding dimensions to reduce constraint complexity.
🔥 Pro Tip 3: Properly name features in the FeatureManager design tree for easier later modifications and team collaboration.
🔥 Pro Tip 4: Use Design Binder or Custom Properties to store drawing numbers, revisions, and other metadata directly in the part file.
⚠️ Common Mistake: Avoid over-defining sketches. If a sketch turns red, you have conflicting constraints or dimensions.
📁 Download Resources
Download all resources for this exercise series:
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Which SolidWorks version do I need for these exercises?
A: Any version from SolidWorks 2018 onwards. Some features might vary slightly.
Q: Can I use these drawings for commercial projects?
A: Yes, all drawings are free to use for personal and commercial purposes with attribution.
Q: How do I verify my model's accuracy?
A: Use Mass Properties tool in SolidWorks or FreeCAD to check volume and surface area against calculated values.
Q: What if my model has different mass properties than expected?
A: Check for: 1) Incorrect dimensions 2) Missing features 3) Extra features 4) Wrong material density settings.
Q: Should I model exactly as drawn or optimize the design?
A: For practice, model exactly as drawn. In real projects, always consider design optimization and manufacturability.
📈 Next Steps After Mastering These Exercises
After completing these practice drawings, we recommend progressing to:
- 💼 Assembly Drawings - how to assemble multiple parts
- 🎨 Photorealistic Rendering - creating professional visualizations
- 📋 Technical Documentation - creating workshop drawings from 3D models
- 🔄 Animation & Motion Study - moving parts and mechanisms
- 🏭 Manufacturing Preparation - CAM integration and DFM analysis
- 🌐 Collaborative Design - working with teams using PDM systems
🎉 Congratulations!
You've successfully completed a comprehensive series of 3D modeling exercises from workshop drawings. Continue practicing with the remaining drawings and challenge yourself with increasingly complex designs!
💬 Discussion & Community
Have questions or want to share your models? Leave a comment below! Join our community of CAD professionals and enthusiasts.
Tags: #SolidWorks #FreeCAD #3DModeling #CAD #Engineering #Tutorial #TechnicalDrawing #WorkshopDrawings #PracticeExercises #MechanicalDesign
Share your results: Post screenshots of your models on social media with #ExtremeSolidWorks